


|
Background |
|
During corrosion of steel reinforcement in concrete corrosion products, mainly iron oxides and iron oxide-hydroxides, form on steel surface. Since corrosion products have larger volume compared to iron their generation can result n additional tensile stresses in the steel/concrete interface leading to concrete cracking and spalling, and eventually structural instability and failure. Time to cracking and the amount of degradation of reinforced concrete structure due to corrosion, strongly depends on the rate of formation, volume and morphology of these corrosion products. |
|
Objective |
|
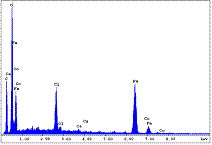
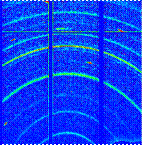
The objective of this project is to perform research on corrosion products formed on corrosion resistant steels in the steel/concrete interface using: - microscopic methods for investigating morphology of corrosion products, - spectroscopic methods for investigating chemical composition of corrosion products, - diffraction methods for investigating crystalline phases in corrosion products, all under the supervision and with the help of highly skilled scientist at the University of California, Berkeley. |


|
Microscopic methods |
|
Spectroscopic methods |
|
Diffraction methods |
|
Recent research of the methods for concrete reinforcement corrosion protection is targeted to development of new types of corrosion resistant steels with lower percentages of alloying elements, which can be a cost-effective corrosion resistant alternative to highly alloyed austenitic stainless steels. Since corrosion products that form on the steel/concrete interface during corrosion play a critical role in cracking and degrading of the concrete, it is of great importance to define them on different types of corrosion resistant steels. Any differences in composition and morphology of corrosion products formed on different types of corrosion resistant steels can lead to differences in stresses created on the steel/concrete interface, consequently leading to differences in time-to-corrosion and degradation of reinforced concrete structures. |

|
List of different corrosion products and their properties |
|
a) Shematic cross section showing reinforcement, layer of corrosion products around reinforcement and concrete; b) Corroded rebar with corrosion products and radial cracks |